Samples Selection with Group Metric for Experience Replay in Continual Learning
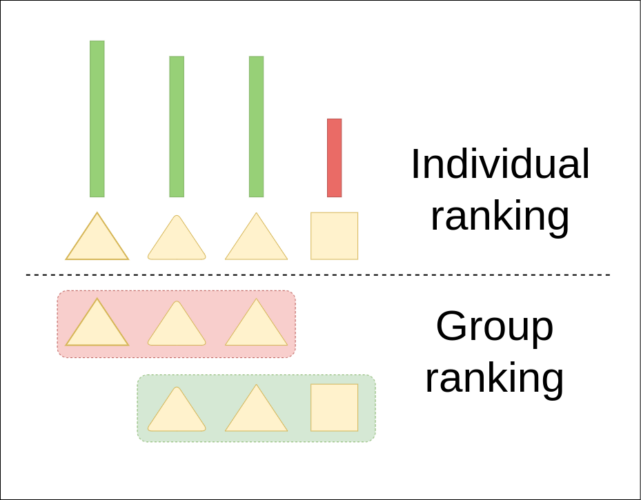
Andrii Krutsylo PhD student at the Institute of Computer Science of the Polish Academy of Sciences The study aims to reduce the decline in performance of a model trained incrementally on non-i.i.d. data, using replay-based strategies to retain previous task knowledge. To address limitations in existing variations, which only select samples based on individual properties, […]
Samples Selection with Group Metric for Experience Replay in Continual Learning Read More »