
CONNECTIVITY FUND
Funded projects
- Meaningful Human Control and Advanced AI Assistants
 Sietze Kai Kuilman PhD at Delft University of Technology Quite recently many large Tech companies have proffered the idea of an Advanced AI Assistant. These assistants should supposedly be able to all manner of tasks for us. They may be able to arrange flight tickets for us, book hotels, order groceries, and plan our agenda’s.… Read more: Meaningful Human Control and Advanced AI Assistants
Sietze Kai Kuilman PhD at Delft University of Technology Quite recently many large Tech companies have proffered the idea of an Advanced AI Assistant. These assistants should supposedly be able to all manner of tasks for us. They may be able to arrange flight tickets for us, book hotels, order groceries, and plan our agenda’s.… Read more: Meaningful Human Control and Advanced AI Assistants - Learning the structure of complex datasets: The case for simplicial complexes
 Antonio G. Marques Professor at King Juan Carlos University Graphs are ubiquitous for modeling the irregular (non-Euclidean) structure of complex data. However, real-world scenarios often involve relationships that span several nodes. While hypergraphs can address such complexities, they lack the mathematical tractability and theoretical foundation of simple graphs. Our strategy for managing these intricate relationships… Read more: Learning the structure of complex datasets: The case for simplicial complexes
Antonio G. Marques Professor at King Juan Carlos University Graphs are ubiquitous for modeling the irregular (non-Euclidean) structure of complex data. However, real-world scenarios often involve relationships that span several nodes. While hypergraphs can address such complexities, they lack the mathematical tractability and theoretical foundation of simple graphs. Our strategy for managing these intricate relationships… Read more: Learning the structure of complex datasets: The case for simplicial complexes - Exploration of Cooperation Factors in Human-Human and Human-AI InteractionsTiffany Matej Hralovic
 Tiffany Matej Hrkalovic PhD Student at Vrije University Amsterdam & Delft University of Technology The enigma of human willingness and ability to cooperate has been a topic of interest for millennia. However, due to the recent technological developments in designing intelligent systems and their potential usage in cooperative settings with humans, newer research is steered… Read more: Exploration of Cooperation Factors in Human-Human and Human-AI InteractionsTiffany Matej Hralovic
Tiffany Matej Hrkalovic PhD Student at Vrije University Amsterdam & Delft University of Technology The enigma of human willingness and ability to cooperate has been a topic of interest for millennia. However, due to the recent technological developments in designing intelligent systems and their potential usage in cooperative settings with humans, newer research is steered… Read more: Exploration of Cooperation Factors in Human-Human and Human-AI InteractionsTiffany Matej Hralovic - Exploring the (Lack of) Cultural Diversity in Multilingual Datasets for NLP
 Lea Krause PhD candidate at Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam The project addresses the critical need for cultural diversity in multilingual datasets used to train and evaluate language models and conversational agents. Current practices often involve translating English-centric content, which limits the cultural authenticity and applicability of these datasets across different regions. For example, evaluating models using… Read more: Exploring the (Lack of) Cultural Diversity in Multilingual Datasets for NLP
Lea Krause PhD candidate at Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam The project addresses the critical need for cultural diversity in multilingual datasets used to train and evaluate language models and conversational agents. Current practices often involve translating English-centric content, which limits the cultural authenticity and applicability of these datasets across different regions. For example, evaluating models using… Read more: Exploring the (Lack of) Cultural Diversity in Multilingual Datasets for NLP - Supervised Learning for Enhancing the Quantum Approximate Optimisation Algorithm
 Zakaria Abdelmoiz Dahi Researcher-Lecturer Quantum computation is based on quantum mechanics principles, which allows it to gain a computational speedup over its classical counterpart, especially in combinatorial optimisation. The Quantum Approximate Optimisation Algorithm (QAOA) is a recent and promising quantum optimisation technique. It is expressed as a parameterisable quantum circuit whose parameters control its efficiency.… Read more: Supervised Learning for Enhancing the Quantum Approximate Optimisation Algorithm
Zakaria Abdelmoiz Dahi Researcher-Lecturer Quantum computation is based on quantum mechanics principles, which allows it to gain a computational speedup over its classical counterpart, especially in combinatorial optimisation. The Quantum Approximate Optimisation Algorithm (QAOA) is a recent and promising quantum optimisation technique. It is expressed as a parameterisable quantum circuit whose parameters control its efficiency.… Read more: Supervised Learning for Enhancing the Quantum Approximate Optimisation Algorithm - A human perceptual metric based on a Riemannian geodesic distance in the probability-extended image domain
 Alexander Hepburn Postdoc at University of Bristol Perceptual distances model a distance between two images, and are often designed to replicate certain processes in the human visual system, or optimised to mimic the decisions in a set of human perceptual judgements. Assuming Barlows hypothesis, that the brain seeks to minimise the amount of redundant information… Read more: A human perceptual metric based on a Riemannian geodesic distance in the probability-extended image domain
Alexander Hepburn Postdoc at University of Bristol Perceptual distances model a distance between two images, and are often designed to replicate certain processes in the human visual system, or optimised to mimic the decisions in a set of human perceptual judgements. Assuming Barlows hypothesis, that the brain seeks to minimise the amount of redundant information… Read more: A human perceptual metric based on a Riemannian geodesic distance in the probability-extended image domain - Trustworthy Probabilistic Machine Learning Models
 Stefano Teso Senior Assistant Professor at CIMeC and DISI, University of Trento There is an increasing need of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) models that can reliably output predictions matching our expectations. Models learned from data should comply with specifications of desirable behavior supplied or elicited from humans and avoid overconfidence, i.e., being… Read more: Trustworthy Probabilistic Machine Learning Models
Stefano Teso Senior Assistant Professor at CIMeC and DISI, University of Trento There is an increasing need of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) models that can reliably output predictions matching our expectations. Models learned from data should comply with specifications of desirable behavior supplied or elicited from humans and avoid overconfidence, i.e., being… Read more: Trustworthy Probabilistic Machine Learning Models - Leveraging Uncertainty for Improved Model Performance
 Luuk de Jong Master student at Universiteit Leiden This project investigates the integration of a reject option in machine learning models to enhance reliability and explainability. By rejecting uncertain predictions, we can mitigate risks associated with low-confidence decisions, meaning the model will be more reliable. The core contribution of this work is the development and… Read more: Leveraging Uncertainty for Improved Model Performance
Luuk de Jong Master student at Universiteit Leiden This project investigates the integration of a reject option in machine learning models to enhance reliability and explainability. By rejecting uncertain predictions, we can mitigate risks associated with low-confidence decisions, meaning the model will be more reliable. The core contribution of this work is the development and… Read more: Leveraging Uncertainty for Improved Model Performance - TEC4CPC – Towards a Trustworthy and Efficient Companion for Car Part Catalogs
 Patrick Lang B.Sc. at N4 N4, a leading provider of procurement platforms in the automotive sector, is facing the challenge of making its catalogs for car parts (N4Parts) more user-friendly. These catalogs are used by customers both to purchase parts and to obtain information, such as installation instructions and maintenance intervals. The use of such… Read more: TEC4CPC – Towards a Trustworthy and Efficient Companion for Car Part Catalogs
Patrick Lang B.Sc. at N4 N4, a leading provider of procurement platforms in the automotive sector, is facing the challenge of making its catalogs for car parts (N4Parts) more user-friendly. These catalogs are used by customers both to purchase parts and to obtain information, such as installation instructions and maintenance intervals. The use of such… Read more: TEC4CPC – Towards a Trustworthy and Efficient Companion for Car Part Catalogs - Reconciling AI explanations with human expectations towards trustworthy AI
 Jeff Clark Research Fellow at the University of Bristol With the widespread deployment of AI systems, it becomes increasingly important that users are equipped to scrutinise these models and their outputs. This is particular true for applications in high stakes domains such as healthcare. We propose to conduct research in the context of explainable AI,… Read more: Reconciling AI explanations with human expectations towards trustworthy AI
Jeff Clark Research Fellow at the University of Bristol With the widespread deployment of AI systems, it becomes increasingly important that users are equipped to scrutinise these models and their outputs. This is particular true for applications in high stakes domains such as healthcare. We propose to conduct research in the context of explainable AI,… Read more: Reconciling AI explanations with human expectations towards trustworthy AI - The European ecosystem of Large Language Models
 Dan Saattrup Nielsen PhD student at Alexandra Instituttet Presentation on the benchmarking of LLMs, with a specific application to the Northern European languages. The challenges of evaluating generative language models, the different ways in which this can be done, and the current status within the Northern European language will be presented. This is followed by… Read more: The European ecosystem of Large Language Models
Dan Saattrup Nielsen PhD student at Alexandra Instituttet Presentation on the benchmarking of LLMs, with a specific application to the Northern European languages. The challenges of evaluating generative language models, the different ways in which this can be done, and the current status within the Northern European language will be presented. This is followed by… Read more: The European ecosystem of Large Language Models - Alzheimer’s Diagnosis: Multimodal Explainable AI for Early Detection and Personalized Care
 Nadeem Qazi Senior Lecturer in AI machine learning at University of East London,UK Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is becoming more common, emphasizing the need for early detection and prediction to improve patient outcomes. Current diagnostic methods are often too late, missing the opportunity for early intervention. This research seeks to develop advanced explainable AI models that… Read more: Alzheimer’s Diagnosis: Multimodal Explainable AI for Early Detection and Personalized Care
Nadeem Qazi Senior Lecturer in AI machine learning at University of East London,UK Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is becoming more common, emphasizing the need for early detection and prediction to improve patient outcomes. Current diagnostic methods are often too late, missing the opportunity for early intervention. This research seeks to develop advanced explainable AI models that… Read more: Alzheimer’s Diagnosis: Multimodal Explainable AI for Early Detection and Personalized Care - Exploring Prosocial Dynamics in Child-Robot Interactions: Adaptation, Measurement, and Trust
 Ana Isabel Caniço Neto Assistant Researcher at the University of Lisbon Social robots are increasingly finding application in diverse settings, including our homes and schools, thus exposing children to interactions with multiple robots individually or in groups. Understanding how to design robots that can effectively interact and cooperate with children in these hybrid groups, in… Read more: Exploring Prosocial Dynamics in Child-Robot Interactions: Adaptation, Measurement, and Trust
Ana Isabel Caniço Neto Assistant Researcher at the University of Lisbon Social robots are increasingly finding application in diverse settings, including our homes and schools, thus exposing children to interactions with multiple robots individually or in groups. Understanding how to design robots that can effectively interact and cooperate with children in these hybrid groups, in… Read more: Exploring Prosocial Dynamics in Child-Robot Interactions: Adaptation, Measurement, and Trust - Types of Contamination in AI Evaluation: Reasoning and Triangulation
 Behzad Mehrbakhsh PhD student at Universitat Politècnica de València A comprehensive and accurate evaluation of AI systems is indispensable for advancing the field and fostering a trustworthy AI ecosystem. AI evaluation results have a significant impact on both academic research and industrial applications, ultimately determining which products or services are deemed effective, safe and reliable… Read more: Types of Contamination in AI Evaluation: Reasoning and Triangulation
Behzad Mehrbakhsh PhD student at Universitat Politècnica de València A comprehensive and accurate evaluation of AI systems is indispensable for advancing the field and fostering a trustworthy AI ecosystem. AI evaluation results have a significant impact on both academic research and industrial applications, ultimately determining which products or services are deemed effective, safe and reliable… Read more: Types of Contamination in AI Evaluation: Reasoning and Triangulation - The European ecosystem of Large Language Models
 Stefanie Baade Deputy Managing Director at German AI Association Presentation of the German AI Association’s efforts to build a European LLM ecosystem. The development of strong, competitive LLMs ‘made in Europe’ often fails due to the necessary access to compute time. Instead, we rely heavily on providers in China and the US. A strong European… Read more: The European ecosystem of Large Language Models
Stefanie Baade Deputy Managing Director at German AI Association Presentation of the German AI Association’s efforts to build a European LLM ecosystem. The development of strong, competitive LLMs ‘made in Europe’ often fails due to the necessary access to compute time. Instead, we rely heavily on providers in China and the US. A strong European… Read more: The European ecosystem of Large Language Models - CLAIRE | Rising Research Network: AI Research and Mental Well-Being Workshop 2nd edition
 Marie Anastacio PhD candidate at Leiden University, RWTH Aachen After the successful execution of our 2023 workshop in collaboration with the TAILOR-ESSAI Summer School, we propose to organise a second edition at ESSAI2024. The event will focus on fostering a community of young AI researchers in Europe, supporting AI researchers and promoting mental well-being for… Read more: CLAIRE | Rising Research Network: AI Research and Mental Well-Being Workshop 2nd edition
Marie Anastacio PhD candidate at Leiden University, RWTH Aachen After the successful execution of our 2023 workshop in collaboration with the TAILOR-ESSAI Summer School, we propose to organise a second edition at ESSAI2024. The event will focus on fostering a community of young AI researchers in Europe, supporting AI researchers and promoting mental well-being for… Read more: CLAIRE | Rising Research Network: AI Research and Mental Well-Being Workshop 2nd edition - Machine Learning Modalities for Materials Science
 Milica Todorovic Associate professor at University of Turku In the past decade, artificial intelligence algorithms have demonstrated a tremendous potential and impact in speeding up the processing, optimisation, and discovery of new materials. The objective of the workshop and school “Machine Learning Modalities for Materials Science” (MLM4MS 2024) was to bring together the community of… Read more: Machine Learning Modalities for Materials Science
Milica Todorovic Associate professor at University of Turku In the past decade, artificial intelligence algorithms have demonstrated a tremendous potential and impact in speeding up the processing, optimisation, and discovery of new materials. The objective of the workshop and school “Machine Learning Modalities for Materials Science” (MLM4MS 2024) was to bring together the community of… Read more: Machine Learning Modalities for Materials Science - Evaluating the Trustworthiness of Human-like Robotic Motion
 Filipa Correia Assistant Researcher at Interactive Technologies Institute, University of Lisbon The research project will explore the trustworthiness of an embodied AI, such as a social robot. Specifically, it will investigate whether the performance of humanlike motions of a non-humanoid robot enhances the perceived trustworthiness of that robot. Beyond the scientific contribution to the current… Read more: Evaluating the Trustworthiness of Human-like Robotic Motion
Filipa Correia Assistant Researcher at Interactive Technologies Institute, University of Lisbon The research project will explore the trustworthiness of an embodied AI, such as a social robot. Specifically, it will investigate whether the performance of humanlike motions of a non-humanoid robot enhances the perceived trustworthiness of that robot. Beyond the scientific contribution to the current… Read more: Evaluating the Trustworthiness of Human-like Robotic Motion - Explanations and Reasoning: Proofs and Models of Intuitionistic Modal Logics
 Philippe Balbiani CNRS researcher at Toulouse Institute of Computer Science Research (Toulouse, France) Rooted in Intuitionistic and Constructive Reasoning, Intermediate Logics have found important applications through the Curry-Howard correspondence. Nowadays, there is an Intuitionistic Modal Logics renaissance in Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence. Connections between, on one hand, Intuitionistic and Constructive Mathematics and, on the… Read more: Explanations and Reasoning: Proofs and Models of Intuitionistic Modal Logics
Philippe Balbiani CNRS researcher at Toulouse Institute of Computer Science Research (Toulouse, France) Rooted in Intuitionistic and Constructive Reasoning, Intermediate Logics have found important applications through the Curry-Howard correspondence. Nowadays, there is an Intuitionistic Modal Logics renaissance in Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence. Connections between, on one hand, Intuitionistic and Constructive Mathematics and, on the… Read more: Explanations and Reasoning: Proofs and Models of Intuitionistic Modal Logics - Neuro-symbolic integration for graph data
 Manfred Jaeger Associate Professor at Aalborg University Learning and reasoning with graph and network data has developed as an area of increasing importance over recent years. Social networks, knowledge graphs, sensor and traffic networks are only some of the examples where graph-structured data arises in important applications. Much of the attention currently focuses on graph… Read more: Neuro-symbolic integration for graph data
Manfred Jaeger Associate Professor at Aalborg University Learning and reasoning with graph and network data has developed as an area of increasing importance over recent years. Social networks, knowledge graphs, sensor and traffic networks are only some of the examples where graph-structured data arises in important applications. Much of the attention currently focuses on graph… Read more: Neuro-symbolic integration for graph data - Improving Cross-Lingual Retrieval of Previously Fact-Checked Claims
 Róbert Móro Researcher at Kempelen Institute of Intelligent Technologies To mitigate disinformation with AI in a trustworthy way, it should prioritize human agency and control, transparency, and accountability including the means for redress. This can be achieved by using AI to support rather than to replace media professionals, such as fact-checkers, in their efforts to… Read more: Improving Cross-Lingual Retrieval of Previously Fact-Checked Claims
Róbert Móro Researcher at Kempelen Institute of Intelligent Technologies To mitigate disinformation with AI in a trustworthy way, it should prioritize human agency and control, transparency, and accountability including the means for redress. This can be achieved by using AI to support rather than to replace media professionals, such as fact-checkers, in their efforts to… Read more: Improving Cross-Lingual Retrieval of Previously Fact-Checked Claims - AI/TP Methods for maximizing generality and tractability of algebras
 Gonçalo Gomes Araújo PhD at Nova FCT We value a mathematical theory for its generality and its tractability. For example, a magma (that is, a set with a binary operation) is very general because any theorem on it will have an impact on almost all algebras and possibly beyond, but the structure is so weak… Read more: AI/TP Methods for maximizing generality and tractability of algebras
Gonçalo Gomes Araújo PhD at Nova FCT We value a mathematical theory for its generality and its tractability. For example, a magma (that is, a set with a binary operation) is very general because any theorem on it will have an impact on almost all algebras and possibly beyond, but the structure is so weak… Read more: AI/TP Methods for maximizing generality and tractability of algebras - Enhancing Reliability and Trustworthiness in IoT Applications through Deep Learning-Based Data Imputation Techniques
 Hakob Grigoryan PhD at NVISION With the evolution of intelligent sensing devices and the Internet of Things (IoT), a vast amount of data is generated from various sources, including sensors, cameras, and network infrastructures, and is transmitted to servers for analysis. Data streaming from sensors in IoT systems might face quality issues like incompleteness due… Read more: Enhancing Reliability and Trustworthiness in IoT Applications through Deep Learning-Based Data Imputation Techniques
Hakob Grigoryan PhD at NVISION With the evolution of intelligent sensing devices and the Internet of Things (IoT), a vast amount of data is generated from various sources, including sensors, cameras, and network infrastructures, and is transmitted to servers for analysis. Data streaming from sensors in IoT systems might face quality issues like incompleteness due… Read more: Enhancing Reliability and Trustworthiness in IoT Applications through Deep Learning-Based Data Imputation Techniques - Exploring Intrusion Detection Knowledge Transfer Between Network Environments
 Patrik Goldschmidt PhD candidate at Kempelen Institute of Intelligent Technologies With the rise of information technology and the Internet, the number of cybersecurity incidents has grown immensely. As a response, the research area of Intrusion Detection Systems (IDSs), aiming to detect and mitigate cyber threats, has gained significant attention. Our research focuses on Network IDSs… Read more: Exploring Intrusion Detection Knowledge Transfer Between Network Environments
Patrik Goldschmidt PhD candidate at Kempelen Institute of Intelligent Technologies With the rise of information technology and the Internet, the number of cybersecurity incidents has grown immensely. As a response, the research area of Intrusion Detection Systems (IDSs), aiming to detect and mitigate cyber threats, has gained significant attention. Our research focuses on Network IDSs… Read more: Exploring Intrusion Detection Knowledge Transfer Between Network Environments - Enhancing Trustworthiness in Healthcare Large Language Models
 Muhammad Waseem Postdoctoral Researcher at Faculty of Information Technology, University of Jyväskylä, Jyväskylä, Finland Large Language Models (LLMs) are advanced AI tools capable of understanding and generating human-like text, advancing various sectors, including healthcare. This project aims to enhance healthcare services using LLMs, focusing on improving their trustworthiness for clinical applications. Trustworthiness encompasses reliability, fairness,… Read more: Enhancing Trustworthiness in Healthcare Large Language Models
Muhammad Waseem Postdoctoral Researcher at Faculty of Information Technology, University of Jyväskylä, Jyväskylä, Finland Large Language Models (LLMs) are advanced AI tools capable of understanding and generating human-like text, advancing various sectors, including healthcare. This project aims to enhance healthcare services using LLMs, focusing on improving their trustworthiness for clinical applications. Trustworthiness encompasses reliability, fairness,… Read more: Enhancing Trustworthiness in Healthcare Large Language Models - Continual Self-Supervised Learning
 Giacomo Cignoni Research Fellow at the University of Pisa Learning continually from non-stationary data streams is a challenging research topic of growing popularity in the last few years. Being able to learn, adapt and generalize continually, in an efficient way appears to be fundamental for a more sustainable development of Artificial Intelligent systems. However, research… Read more: Continual Self-Supervised Learning
Giacomo Cignoni Research Fellow at the University of Pisa Learning continually from non-stationary data streams is a challenging research topic of growing popularity in the last few years. Being able to learn, adapt and generalize continually, in an efficient way appears to be fundamental for a more sustainable development of Artificial Intelligent systems. However, research… Read more: Continual Self-Supervised Learning - Tractable and Explainable Probabilistic AI
 Lennert De Smet PhD at KU Leuven Transparency and technical robustness are two fundamental requirements for AI systems following the European Union AI Act, especially in higher-risk domains. Transparency is intricately related to the notion of explainability, allowing an AI system to accurately describe the reasoning behind its predictions. Through such explanations does the system… Read more: Tractable and Explainable Probabilistic AI
Lennert De Smet PhD at KU Leuven Transparency and technical robustness are two fundamental requirements for AI systems following the European Union AI Act, especially in higher-risk domains. Transparency is intricately related to the notion of explainability, allowing an AI system to accurately describe the reasoning behind its predictions. Through such explanations does the system… Read more: Tractable and Explainable Probabilistic AI - Trustworthy, Ethical and Beneficial-to-All Multiagent Systems Solutions for Social Ridesharing and the Hospitality Industry
 Georgios Chalkiadakis Professor at Technical University of Crete Current mobility-as-a-service platforms have departed from the original objectives of the sharing economy-inspired social ridesharing paradigm: regrettably, they view drivers as taxi workers; focus on profit maximization rather than fair travel costs’ allocation; and disregard essential private preferences of users (relating for instance to their feeling of… Read more: Trustworthy, Ethical and Beneficial-to-All Multiagent Systems Solutions for Social Ridesharing and the Hospitality Industry
Georgios Chalkiadakis Professor at Technical University of Crete Current mobility-as-a-service platforms have departed from the original objectives of the sharing economy-inspired social ridesharing paradigm: regrettably, they view drivers as taxi workers; focus on profit maximization rather than fair travel costs’ allocation; and disregard essential private preferences of users (relating for instance to their feeling of… Read more: Trustworthy, Ethical and Beneficial-to-All Multiagent Systems Solutions for Social Ridesharing and the Hospitality Industry - Translating between AI Evaluation and Job Tasks in the human workplace for trustworthy and reliable AI deployment
 Marko Tesic Post-doc at LCFI, University of Cambridge, UK Recent advancements in AI, particularly in language modeling, have rekindled concerns about the potential automation of certain roles within the human workforce. To better understand which roles are susceptible to automation and to ensure the trustworthy and reliable deployment of AI, I aim to establish a… Read more: Translating between AI Evaluation and Job Tasks in the human workplace for trustworthy and reliable AI deployment
Marko Tesic Post-doc at LCFI, University of Cambridge, UK Recent advancements in AI, particularly in language modeling, have rekindled concerns about the potential automation of certain roles within the human workforce. To better understand which roles are susceptible to automation and to ensure the trustworthy and reliable deployment of AI, I aim to establish a… Read more: Translating between AI Evaluation and Job Tasks in the human workplace for trustworthy and reliable AI deployment - Evaluation of cognitive capabilities for LLMs
 Lorenzo Pacchiardi Post-doc at University of Cambridge Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems (such as reinforcement-learning agents and Large Language Models, or LLMs) are typically evaluated by testing them on a benchmark and reporting an aggregated score. As benchmarks are constituted of instances demanding various capability levels to be completed, the aggregated score is uninformative of the… Read more: Evaluation of cognitive capabilities for LLMs
Lorenzo Pacchiardi Post-doc at University of Cambridge Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems (such as reinforcement-learning agents and Large Language Models, or LLMs) are typically evaluated by testing them on a benchmark and reporting an aggregated score. As benchmarks are constituted of instances demanding various capability levels to be completed, the aggregated score is uninformative of the… Read more: Evaluation of cognitive capabilities for LLMs - Large Language Models for Media and Democracy: Wrecking or Saving Society?
 Davide Ceolin, Piek Vossen, Ilia Markov, Catholijn Jonker, Pradeep Murukannaiah Senior Researcher (Ceolin), Full Professor (Vossen, Jonker), Assistant Professor (Markov, Murukannaiah) Over the past years, foundational models, including large-language models and multi-modal systems, have significantly advanced the possibilities regarding the understanding, analysis, and generation of human language. However, from the extensive and widespread use of… Read more: Large Language Models for Media and Democracy: Wrecking or Saving Society?
Davide Ceolin, Piek Vossen, Ilia Markov, Catholijn Jonker, Pradeep Murukannaiah Senior Researcher (Ceolin), Full Professor (Vossen, Jonker), Assistant Professor (Markov, Murukannaiah) Over the past years, foundational models, including large-language models and multi-modal systems, have significantly advanced the possibilities regarding the understanding, analysis, and generation of human language. However, from the extensive and widespread use of… Read more: Large Language Models for Media and Democracy: Wrecking or Saving Society? - Ilia Markov
 Ilia Markov Assistant Professor at Computational Linguistics & Text Mining Lab, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam Ilia Markov is an Assistant Professor at the Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam. His research interests include hate speech detection, generation of counter-narratives against hate speech, and authorship analysis-related tasks such as authorship attribution and author profiling. Scientific area: Computational Linguistics, Natural Language… Read more: Ilia Markov
Ilia Markov Assistant Professor at Computational Linguistics & Text Mining Lab, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam Ilia Markov is an Assistant Professor at the Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam. His research interests include hate speech detection, generation of counter-narratives against hate speech, and authorship analysis-related tasks such as authorship attribution and author profiling. Scientific area: Computational Linguistics, Natural Language… Read more: Ilia Markov - Grounded World Models for Higher Layers of Meaning
 Stefano de Giorgis Post-doc researcher at Institute for Cognitive Sciences and Technologies – National Research Council (ISTC-CNR), Italy The project involves knowledge representation techniques, neuro-simbolic AI, and cognitive semantics. According to the embodied cognition principles, individuals construct a cognitive representation and conceptualization of the external world based on their perceptual capabilities, according to their affordances,… Read more: Grounded World Models for Higher Layers of Meaning
Stefano de Giorgis Post-doc researcher at Institute for Cognitive Sciences and Technologies – National Research Council (ISTC-CNR), Italy The project involves knowledge representation techniques, neuro-simbolic AI, and cognitive semantics. According to the embodied cognition principles, individuals construct a cognitive representation and conceptualization of the external world based on their perceptual capabilities, according to their affordances,… Read more: Grounded World Models for Higher Layers of Meaning - Multi-agent scheduling in a human-robot collaborative warehouse
 Bram Renting PhD at Leiden University, Delft University of Technology In cooperative multi-agent environments, agents can be interdependent in completing tasks. We consider environments where agents schedule future interactions with others they depend on to perform the task. More specifically, our project focuses on human-robot warehouses where humans pick products from shelves and robots transport… Read more: Multi-agent scheduling in a human-robot collaborative warehouse
Bram Renting PhD at Leiden University, Delft University of Technology In cooperative multi-agent environments, agents can be interdependent in completing tasks. We consider environments where agents schedule future interactions with others they depend on to perform the task. More specifically, our project focuses on human-robot warehouses where humans pick products from shelves and robots transport… Read more: Multi-agent scheduling in a human-robot collaborative warehouse - Evolution of Theory of Mind
 Harmen de Weerd Assistant Professor at University of Groningen In social interactions, humans often make use of their “theory of mind”, which refers to their ability to reason about unobservable mental content of others. Humans can even use their theory of mind to reason about the way other use theory of mind. However, such higher-order… Read more: Evolution of Theory of Mind
Harmen de Weerd Assistant Professor at University of Groningen In social interactions, humans often make use of their “theory of mind”, which refers to their ability to reason about unobservable mental content of others. Humans can even use their theory of mind to reason about the way other use theory of mind. However, such higher-order… Read more: Evolution of Theory of Mind - AI Safety Working group – European kickoff workshop
 Xavier Fresquet Deputy Director, PhD at Sorbonne Université AI systems offer the potential for substantial benefits to society but they are not without risks, such as toxicity, misinformation, and bias. As with other complex technologies, society needs industry-standard safety testing to realize the benefits while minimizing the risks. To address this problem, an AI Safety… Read more: AI Safety Working group – European kickoff workshop
Xavier Fresquet Deputy Director, PhD at Sorbonne Université AI systems offer the potential for substantial benefits to society but they are not without risks, such as toxicity, misinformation, and bias. As with other complex technologies, society needs industry-standard safety testing to realize the benefits while minimizing the risks. To address this problem, an AI Safety… Read more: AI Safety Working group – European kickoff workshop - Building trust in administrative automation through the use of LLMs in the public sector of Sweden
 Niclas Willem Fock CEO Santa Anna IT Research Insititute, Sweden (Linköping University, Department of Electrical Engineering) Introduction: Santa Anna IT Research Institute (“Santa Anna”) has through its membership in the consortium “AI Sweden” collaborated on the development of the GPT-SW3: LLMs. The GPT-SW3: models are since November 2023 open for further development, research and applications.… Read more: Building trust in administrative automation through the use of LLMs in the public sector of Sweden
Niclas Willem Fock CEO Santa Anna IT Research Insititute, Sweden (Linköping University, Department of Electrical Engineering) Introduction: Santa Anna IT Research Institute (“Santa Anna”) has through its membership in the consortium “AI Sweden” collaborated on the development of the GPT-SW3: LLMs. The GPT-SW3: models are since November 2023 open for further development, research and applications.… Read more: Building trust in administrative automation through the use of LLMs in the public sector of Sweden - Eindhoven- Leuven – Aachen AI Workshop Series on Secure, Reliable and Trustworthy AI
 Alexa Kodde Project Manager at CLAIRE CLAIRE aims to provide organisational and logistical coordination and support, as well as promotion and visibility, for the planned AI Workshop Series on Secure, Reliable and Trustworthy AI, hosted by Eindhoven University of Technology, KU Leuven, and RWTH Aachen University. The overarching objective is to not only strengthen regional,… Read more: Eindhoven- Leuven – Aachen AI Workshop Series on Secure, Reliable and Trustworthy AI
Alexa Kodde Project Manager at CLAIRE CLAIRE aims to provide organisational and logistical coordination and support, as well as promotion and visibility, for the planned AI Workshop Series on Secure, Reliable and Trustworthy AI, hosted by Eindhoven University of Technology, KU Leuven, and RWTH Aachen University. The overarching objective is to not only strengthen regional,… Read more: Eindhoven- Leuven – Aachen AI Workshop Series on Secure, Reliable and Trustworthy AI - Europe’s Moonshot Ambition in AI: Vision & Implementation
 Alexa Kodde Project Manager at CLAIRE AI is the primary driver of scientific discoveries, industrial engineering, energy production, logistics, the creative economy, education, and public services. The vision for “AI Made in Europe” is more important than ever. But are we sure the vision has not become “AI Made Elsewhere”? Keywords: AI; moonshot; sovereignty Scientific… Read more: Europe’s Moonshot Ambition in AI: Vision & Implementation
Alexa Kodde Project Manager at CLAIRE AI is the primary driver of scientific discoveries, industrial engineering, energy production, logistics, the creative economy, education, and public services. The vision for “AI Made in Europe” is more important than ever. But are we sure the vision has not become “AI Made Elsewhere”? Keywords: AI; moonshot; sovereignty Scientific… Read more: Europe’s Moonshot Ambition in AI: Vision & Implementation - An Adaptive Initial Design for Bayesian Optimization
 Carolin Benjamins PhD at Leibniz University Hannover Our goal is to progress on Dynamic Algorithm Configuration (DAC) for Bayesian Optimization (BO). BO is a widely-used and sample-efficient framework for optimizing black-box problems, which are often expensive to evaluate. Dynamically configuring BO enables to adapt to the optimization progress and to any problem landscape without prior… Read more: An Adaptive Initial Design for Bayesian Optimization
Carolin Benjamins PhD at Leibniz University Hannover Our goal is to progress on Dynamic Algorithm Configuration (DAC) for Bayesian Optimization (BO). BO is a widely-used and sample-efficient framework for optimizing black-box problems, which are often expensive to evaluate. Dynamically configuring BO enables to adapt to the optimization progress and to any problem landscape without prior… Read more: An Adaptive Initial Design for Bayesian Optimization - Leveraging Social Agents as Mediators to Foster Trust and Comprehension of Affective Engagement with Digital Content
 Sergio Muñoz Assistant Professor at Universidad Politécnica de Madrid The vast and ever-expanding digital landscape presents significant challenges for users striving to navigate and discern accurate information. This challenge is compounded by the dynamic nature of the Internet, characterized by attention-seeking strategies intended to exploit users’ unconscious emotional responses. This affects the credibility of information… Read more: Leveraging Social Agents as Mediators to Foster Trust and Comprehension of Affective Engagement with Digital Content
Sergio Muñoz Assistant Professor at Universidad Politécnica de Madrid The vast and ever-expanding digital landscape presents significant challenges for users striving to navigate and discern accurate information. This challenge is compounded by the dynamic nature of the Internet, characterized by attention-seeking strategies intended to exploit users’ unconscious emotional responses. This affects the credibility of information… Read more: Leveraging Social Agents as Mediators to Foster Trust and Comprehension of Affective Engagement with Digital Content - Improving Multi-Task Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning Methods
 Róbert Belanec PhD at Kempelen Institute of Intelligent Technologies The trustworthiness of the generative AI models is an important topic, especially with the increase in popularity of generative large language models. In recent years, the transformer architecture has become popular in the field of natural language processing. However, the increase in parameters is reducing the… Read more: Improving Multi-Task Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning Methods
Róbert Belanec PhD at Kempelen Institute of Intelligent Technologies The trustworthiness of the generative AI models is an important topic, especially with the increase in popularity of generative large language models. In recent years, the transformer architecture has become popular in the field of natural language processing. However, the increase in parameters is reducing the… Read more: Improving Multi-Task Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning Methods - Explainable Semi-Supervised Fuzzy C-Means
 Kamil Kmita Research Assistant at Systems Research Institute, Polish Academy of Sciences Semi-Supervised Fuzzy C-Means (SSFCMeans) model adapts an unsupervised fuzzy clustering algorithm to handle partial supervision in the form of categorical labels. One of the key challenges is to appropriately handle the impact of partial supervision (IPS) on the outcomes of the model. SSFCMeans… Read more: Explainable Semi-Supervised Fuzzy C-Means
Kamil Kmita Research Assistant at Systems Research Institute, Polish Academy of Sciences Semi-Supervised Fuzzy C-Means (SSFCMeans) model adapts an unsupervised fuzzy clustering algorithm to handle partial supervision in the form of categorical labels. One of the key challenges is to appropriately handle the impact of partial supervision (IPS) on the outcomes of the model. SSFCMeans… Read more: Explainable Semi-Supervised Fuzzy C-Means - The First Workshop on Hybrid Human-Machine Learning and Decision Making
 Andrea Passerini Associate professor at University of Trento In the past, machine learning and decision-making have been treated as independent research areas. However, with the increasing emphasis on human-centered AI, there has been a growing interest in combining these two areas. Researchers have explored approaches that aim to complement human decision-making rather than replace it,… Read more: The First Workshop on Hybrid Human-Machine Learning and Decision Making
Andrea Passerini Associate professor at University of Trento In the past, machine learning and decision-making have been treated as independent research areas. However, with the increasing emphasis on human-centered AI, there has been a growing interest in combining these two areas. Researchers have explored approaches that aim to complement human decision-making rather than replace it,… Read more: The First Workshop on Hybrid Human-Machine Learning and Decision Making - AI for PeopleInternational Conference “AI for People: Democratizing AI”AI for People
 AI for People International nonprofit organization The International Conference “AI for People” was born out of the idea of shaping Artificial Intelligence technology around human and societal needs. While Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be a beneficial tool, its development and its deployment impact society and the environment in ways that need to be thoroughly addressed… Read more: AI for PeopleInternational Conference “AI for People: Democratizing AI”AI for People
AI for People International nonprofit organization The International Conference “AI for People” was born out of the idea of shaping Artificial Intelligence technology around human and societal needs. While Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be a beneficial tool, its development and its deployment impact society and the environment in ways that need to be thoroughly addressed… Read more: AI for PeopleInternational Conference “AI for People: Democratizing AI”AI for People - Robust and safe reinforcement learning against uncertainties in human feedback
 Taku Yamagata Senior Research Associate at the University of Bristol Abstract One of the promising approaches to improve the robustness and safety of reinforcement learning (RL) is collecting human feedback and, that way, incorporating prior knowledge of the target environment. However, human feedback can be inconsistent and infrequent. In this proposed research visit, we explore… Read more: Robust and safe reinforcement learning against uncertainties in human feedback
Taku Yamagata Senior Research Associate at the University of Bristol Abstract One of the promising approaches to improve the robustness and safety of reinforcement learning (RL) is collecting human feedback and, that way, incorporating prior knowledge of the target environment. However, human feedback can be inconsistent and infrequent. In this proposed research visit, we explore… Read more: Robust and safe reinforcement learning against uncertainties in human feedback - Holistic Evaluation of AI-assisted Biomedicine: A Case study on Interactive Cell Segmentation
 Wout Schellaert PhD student at Universitat Politècnica de València Abstract Rapid advances in artificial intelligence have resulted in a correspondingly growing prominence of AI-based tools in day to day biomedicine workflows. As a high-risk domain with impact on human health, it is of vital importance that any AI systems in use are reliable, safe, and… Read more: Holistic Evaluation of AI-assisted Biomedicine: A Case study on Interactive Cell Segmentation
Wout Schellaert PhD student at Universitat Politècnica de València Abstract Rapid advances in artificial intelligence have resulted in a correspondingly growing prominence of AI-based tools in day to day biomedicine workflows. As a high-risk domain with impact on human health, it is of vital importance that any AI systems in use are reliable, safe, and… Read more: Holistic Evaluation of AI-assisted Biomedicine: A Case study on Interactive Cell Segmentation - 1st ContinualAI Unconference
 Vincenzo Lo Monaco Assistant Professor and ContinualAI President Abstract Organized by the non-profit research organization ContinualAI, the conference aims at speeding-up the long desired inclusive and sustainable progress of our community with an open-access, multi-timezone, 24 hours long event which brings together ideas at the intersection of machine learning, computational neuroscience, robotics and more! The… Read more: 1st ContinualAI Unconference
Vincenzo Lo Monaco Assistant Professor and ContinualAI President Abstract Organized by the non-profit research organization ContinualAI, the conference aims at speeding-up the long desired inclusive and sustainable progress of our community with an open-access, multi-timezone, 24 hours long event which brings together ideas at the intersection of machine learning, computational neuroscience, robotics and more! The… Read more: 1st ContinualAI Unconference - CLAIRE | Rising Research Network: AI Research and Mental Well-Being Workshop
 Nicolò Brandizzi PhD student at Sapienza University of Rome Abstract The rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) research and applications have emphasized the need for collaboration between academia and industry, especially among new AI researchers. Such collaborations drive innovation, translate research into practical solutions, and address sector-specific challenges. The CLAIRE Rising Researcher Network (R2Net) aims… Read more: CLAIRE | Rising Research Network: AI Research and Mental Well-Being Workshop
Nicolò Brandizzi PhD student at Sapienza University of Rome Abstract The rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) research and applications have emphasized the need for collaboration between academia and industry, especially among new AI researchers. Such collaborations drive innovation, translate research into practical solutions, and address sector-specific challenges. The CLAIRE Rising Researcher Network (R2Net) aims… Read more: CLAIRE | Rising Research Network: AI Research and Mental Well-Being Workshop - Fostering Appropriate Trust in Predictive Policing AI Systems
 Siddharth Mehrotra PhD student at TU Delft The use of AI in law enforcement, particularly in predictive policing, raises concerns about bias, discrimination, and infringement of civil liberties. Building appropriate trust in these systems is crucial to address these concerns and ensure ethical use. In this research proposal, we aim to investigate how explanations generated… Read more: Fostering Appropriate Trust in Predictive Policing AI Systems
Siddharth Mehrotra PhD student at TU Delft The use of AI in law enforcement, particularly in predictive policing, raises concerns about bias, discrimination, and infringement of civil liberties. Building appropriate trust in these systems is crucial to address these concerns and ensure ethical use. In this research proposal, we aim to investigate how explanations generated… Read more: Fostering Appropriate Trust in Predictive Policing AI Systems - Meta-learning for Continual Learning
 Anna Vettoruzzo PhD student at the Halmstad University Continual learning (CL) refers to the ability to continually learn over time by accommodating new knowledge while retaining previously learned experiences. While this concept is inherent in the human learning ability, current machine learning-based methods struggle with this as they are highly prone to forget past experiences… Read more: Meta-learning for Continual Learning
Anna Vettoruzzo PhD student at the Halmstad University Continual learning (CL) refers to the ability to continually learn over time by accommodating new knowledge while retaining previously learned experiences. While this concept is inherent in the human learning ability, current machine learning-based methods struggle with this as they are highly prone to forget past experiences… Read more: Meta-learning for Continual Learning - Deep reinforcement learning for predictive monitoring under LTLf constraints
 Efrén Rama Maneiro PhD student at the University of Santiago de Compostela Predictive monitoring is a subfield of process mining that focuses on predicting how a process will unfold. Deep learning techniques have become popular in this field due to their enhanced performance with respect to classic machine learning models. However, most of these approaches… Read more: Deep reinforcement learning for predictive monitoring under LTLf constraints
Efrén Rama Maneiro PhD student at the University of Santiago de Compostela Predictive monitoring is a subfield of process mining that focuses on predicting how a process will unfold. Deep learning techniques have become popular in this field due to their enhanced performance with respect to classic machine learning models. However, most of these approaches… Read more: Deep reinforcement learning for predictive monitoring under LTLf constraints - Data-Centric AutoML and Benchmarks with Optimal Transport
 Prabhant Singh Research Engineer at TU Eindhoven Automated machine learning (AutoML) aims to make easier and more accessible use of machine learning algorithms for researchers with varying levels of expertise. However, AutoML systems, including classical ones such as Auto-Sklearn and Neural Architecture Search (NSGANet, ENAS, DARTS), still face challenges with starting from scratch for their… Read more: Data-Centric AutoML and Benchmarks with Optimal Transport
Prabhant Singh Research Engineer at TU Eindhoven Automated machine learning (AutoML) aims to make easier and more accessible use of machine learning algorithms for researchers with varying levels of expertise. However, AutoML systems, including classical ones such as Auto-Sklearn and Neural Architecture Search (NSGANet, ENAS, DARTS), still face challenges with starting from scratch for their… Read more: Data-Centric AutoML and Benchmarks with Optimal Transport - Multi-Objective Rating Systems
 Paolo Turrini Associate Professor at the Department of Computer Science, University of Warwick This project studies rating systems with multiple objectives, where users are matched to items in order to satisfy several desirable properties. In particular, it looks beyond classical Pareto efficiency, modelling and studying allocations that satisfy fairness, diversity and reliability. This project will… Read more: Multi-Objective Rating Systems
Paolo Turrini Associate Professor at the Department of Computer Science, University of Warwick This project studies rating systems with multiple objectives, where users are matched to items in order to satisfy several desirable properties. In particular, it looks beyond classical Pareto efficiency, modelling and studying allocations that satisfy fairness, diversity and reliability. This project will… Read more: Multi-Objective Rating Systems - Optimal training of a structured ensemble of Binarized Neural Networks with Mixed-Integer Linear Programming techniques
 Simone Milanesi, Ambrogio Maria Bernardelli PhD students at the CompOpt Lab (University of Pavia) Binarized Neural Networks (BNNs) are receiving increasing attention due to their lightweight architecture and ability to run on low-power devices.The Mixed-Integer Linear Programming (MILP) approach achieves the state of the art for training classification BNNs when limited data are available.We propose… Read more: Optimal training of a structured ensemble of Binarized Neural Networks with Mixed-Integer Linear Programming techniques
Simone Milanesi, Ambrogio Maria Bernardelli PhD students at the CompOpt Lab (University of Pavia) Binarized Neural Networks (BNNs) are receiving increasing attention due to their lightweight architecture and ability to run on low-power devices.The Mixed-Integer Linear Programming (MILP) approach achieves the state of the art for training classification BNNs when limited data are available.We propose… Read more: Optimal training of a structured ensemble of Binarized Neural Networks with Mixed-Integer Linear Programming techniques - Open Machine Learning workshop
 Meelis Kull Associate Professor at the University of Tartu he field of Machine Learning continues to grow tremendously and has a significant impact on society. As such, it is important to democratize machine learning, i.e. to make sure that software, datasets, models, and analyses are freely available for easy discovery, verifiability, reproducibility, reuse and meta-analysis.… Read more: Open Machine Learning workshop
Meelis Kull Associate Professor at the University of Tartu he field of Machine Learning continues to grow tremendously and has a significant impact on society. As such, it is important to democratize machine learning, i.e. to make sure that software, datasets, models, and analyses are freely available for easy discovery, verifiability, reproducibility, reuse and meta-analysis.… Read more: Open Machine Learning workshop - Predicting conversational memorability in group interactions: Continual learning approach
 Maria Tsfasman PhD student at TU Delft As AI applications continue to proliferate in our daily lives, the need for social intelligence in these systems becomes increasingly crucial. To enable long-term performance of social intelligence, AI systems must be aware of important moments, or “hotspots” in user conversations. Till now, conversational hotspots have been mainly… Read more: Predicting conversational memorability in group interactions: Continual learning approach
Maria Tsfasman PhD student at TU Delft As AI applications continue to proliferate in our daily lives, the need for social intelligence in these systems becomes increasingly crucial. To enable long-term performance of social intelligence, AI systems must be aware of important moments, or “hotspots” in user conversations. Till now, conversational hotspots have been mainly… Read more: Predicting conversational memorability in group interactions: Continual learning approach - Mastering Natural Language Processing methodologies and technologies
 Mariangela Graziano PhD student at Università degli Studi della Campania “L. Vanvitelli” Natural Language Processing (NLP) is an area of artificial intelligence (AI) that deals with giving computers the ability to understand text and spoken words in the same way that people do. As textual data is now everywhere: documents on our PCs or in… Read more: Mastering Natural Language Processing methodologies and technologies
Mariangela Graziano PhD student at Università degli Studi della Campania “L. Vanvitelli” Natural Language Processing (NLP) is an area of artificial intelligence (AI) that deals with giving computers the ability to understand text and spoken words in the same way that people do. As textual data is now everywhere: documents on our PCs or in… Read more: Mastering Natural Language Processing methodologies and technologies - Mastering Natural Language Processing and Process Mining methodologies and technologies
 Luigi Colucci Cante PhD student at Università degli Studi della Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli” For several years, a very ambitious process has been going on to digitalize the entire public administration system relating to the services offered to the public. In an attempt to facilitate the implementation of this transformation, the use of standards for the… Read more: Mastering Natural Language Processing and Process Mining methodologies and technologies
Luigi Colucci Cante PhD student at Università degli Studi della Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli” For several years, a very ambitious process has been going on to digitalize the entire public administration system relating to the services offered to the public. In an attempt to facilitate the implementation of this transformation, the use of standards for the… Read more: Mastering Natural Language Processing and Process Mining methodologies and technologies - Towards Prototype-Based Explainable Machine Learning for Flood Detection
 Ivica Obadic Chair of Data Science in Earth Observation at the Technical University of Munich The increasingly available high-resolution satellite data has shown to be a valuable resource in tackling pressing issues related to climate change and urbanization such as flood detection. In recent years, deep learning models based on satellite data have shown to be… Read more: Towards Prototype-Based Explainable Machine Learning for Flood Detection
Ivica Obadic Chair of Data Science in Earth Observation at the Technical University of Munich The increasingly available high-resolution satellite data has shown to be a valuable resource in tackling pressing issues related to climate change and urbanization such as flood detection. In recent years, deep learning models based on satellite data have shown to be… Read more: Towards Prototype-Based Explainable Machine Learning for Flood Detection - Samples Selection with Group Metric for Experience Replay in Continual Learning
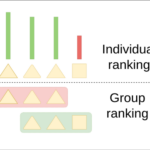 Andrii Krutsylo PhD student at the Institute of Computer Science of the Polish Academy of Sciences The study aims to reduce the decline in performance of a model trained incrementally on non-i.i.d. data, using replay-based strategies to retain previous task knowledge. To address limitations in existing variations, which only select samples based on individual properties,… Read more: Samples Selection with Group Metric for Experience Replay in Continual Learning
Andrii Krutsylo PhD student at the Institute of Computer Science of the Polish Academy of Sciences The study aims to reduce the decline in performance of a model trained incrementally on non-i.i.d. data, using replay-based strategies to retain previous task knowledge. To address limitations in existing variations, which only select samples based on individual properties,… Read more: Samples Selection with Group Metric for Experience Replay in Continual Learning - Large Scale Combinatorial Graybox Optimization
 Lorenzo Canonne PhD student at Inria The field of gray box optimization has led to the design of new operators capable of using the structural information of problems; these operators are now the basis of powerfulmeta-heuristics. For large-scale NK landscapes, many operators have been proposed and iterated local search combined with gray box crossovers is… Read more: Large Scale Combinatorial Graybox Optimization
Lorenzo Canonne PhD student at Inria The field of gray box optimization has led to the design of new operators capable of using the structural information of problems; these operators are now the basis of powerfulmeta-heuristics. For large-scale NK landscapes, many operators have been proposed and iterated local search combined with gray box crossovers is… Read more: Large Scale Combinatorial Graybox Optimization - Making big benchmarks more trustworthy: Identifying the capabilities and limitations of language models by improving the BIG-Bench benchmark
 Ryan Burnell Postdoctoral Research Fellow at Leverhulme Centre for the Future of Intelligence, University of Cambridge, UK AI systems are becoming an integral part of every aspect of modern life. To ensure public trust in these systems, we need tools that can be used to evaluate their capabilities and weaknesses. But these tools are struggling… Read more: Making big benchmarks more trustworthy: Identifying the capabilities and limitations of language models by improving the BIG-Bench benchmark
Ryan Burnell Postdoctoral Research Fellow at Leverhulme Centre for the Future of Intelligence, University of Cambridge, UK AI systems are becoming an integral part of every aspect of modern life. To ensure public trust in these systems, we need tools that can be used to evaluate their capabilities and weaknesses. But these tools are struggling… Read more: Making big benchmarks more trustworthy: Identifying the capabilities and limitations of language models by improving the BIG-Bench benchmark - Learning Neural Algebras
 Pedro Zuidberg Dos Martires Postdoctoral Researcher at Örebro University (Sweden) Abstract algebra provides a formalism to study sets and how the elements of these sets relate to each other by defining relations between set elements. Abstract algebraic structures are abundantly present in artificial intelligence. For instance, Boolean algebra constitutes the bedrock of symbolic AI. Interestingly,… Read more: Learning Neural Algebras
Pedro Zuidberg Dos Martires Postdoctoral Researcher at Örebro University (Sweden) Abstract algebra provides a formalism to study sets and how the elements of these sets relate to each other by defining relations between set elements. Abstract algebraic structures are abundantly present in artificial intelligence. For instance, Boolean algebra constitutes the bedrock of symbolic AI. Interestingly,… Read more: Learning Neural Algebras - Learning trustworthy models from positive and unlabelled data
 Pawel Teisseyre Assistant Professor at the Polish Academy of Sciences The goal of the research stay is to explore learning classification models using positive-unlabelled (PU) data. In PU learning, it is assumed that only some observations in training data are assigned label, which is positive, whereas the remaining observations are unlabelled and can be either… Read more: Learning trustworthy models from positive and unlabelled data
Pawel Teisseyre Assistant Professor at the Polish Academy of Sciences The goal of the research stay is to explore learning classification models using positive-unlabelled (PU) data. In PU learning, it is assumed that only some observations in training data are assigned label, which is positive, whereas the remaining observations are unlabelled and can be either… Read more: Learning trustworthy models from positive and unlabelled data - Imagining the landscape after the AI Act
 Francesca Naretto PhD Student In April 2021, the EU Parliament published a proposal, the AI Act (AIA), for regulating the use of AI systems and services in the Union market. However, the effects of EU digital regulations usually transcend its confines. An example of what has been named the “Brussel effect” – the high impact… Read more: Imagining the landscape after the AI Act
Francesca Naretto PhD Student In April 2021, the EU Parliament published a proposal, the AI Act (AIA), for regulating the use of AI systems and services in the Union market. However, the effects of EU digital regulations usually transcend its confines. An example of what has been named the “Brussel effect” – the high impact… Read more: Imagining the landscape after the AI Act - A Modular Framework for Hybrid Participatory Systems
 Enrico Liscio – TU Delft PhD student Participatory systems aim to elicit citizens’ stances on societal discussions to inform policy making. In particular, human values are a crucial component of citizens’ stances, since they are the drivers of our opinions and behaviors. AI can enable mass participation and process large quantity of citizens’ input. However,… Read more: A Modular Framework for Hybrid Participatory Systems
Enrico Liscio – TU Delft PhD student Participatory systems aim to elicit citizens’ stances on societal discussions to inform policy making. In particular, human values are a crucial component of citizens’ stances, since they are the drivers of our opinions and behaviors. AI can enable mass participation and process large quantity of citizens’ input. However,… Read more: A Modular Framework for Hybrid Participatory Systems - Trustworthy AI for human behavior prediction by autonomous vehicles
 Julian F. Schumann – TU Delft PhD student For humans to trust autonomous vehicles, they need to have confidence in the vehicles’ ability to reliably resolve space-sharing conflicts with other traffic participants in a safe manner – such as in the case of crossing or merging paths. Planning safe and efficient interactions for autonomous vehicles… Read more: Trustworthy AI for human behavior prediction by autonomous vehicles
Julian F. Schumann – TU Delft PhD student For humans to trust autonomous vehicles, they need to have confidence in the vehicles’ ability to reliably resolve space-sharing conflicts with other traffic participants in a safe manner – such as in the case of crossing or merging paths. Planning safe and efficient interactions for autonomous vehicles… Read more: Trustworthy AI for human behavior prediction by autonomous vehicles - Graph Gaussian Processes for Interactive Robot Task Learning
 Giovanni Franzese – TU Delft PhD candidate The adaptability of robot manipulators to many different tasks is currently constrained by systematic hard coding of each specific task. Recent machine learning methods like Learning from Demonstrations (LfD) and Reinforcement Learning (RL) have shown promising results in having fast reprogramming of the task using human demonstrations or… Read more: Graph Gaussian Processes for Interactive Robot Task Learning
Giovanni Franzese – TU Delft PhD candidate The adaptability of robot manipulators to many different tasks is currently constrained by systematic hard coding of each specific task. Recent machine learning methods like Learning from Demonstrations (LfD) and Reinforcement Learning (RL) have shown promising results in having fast reprogramming of the task using human demonstrations or… Read more: Graph Gaussian Processes for Interactive Robot Task Learning - Multi-Objective Statistically Robust Algorithm Ranking
 Jeroen G. Rook – University of Twente PhD candidate Comparing algorithms is a non-trivial task. Often, a set of representative problem instances are used to compare algorithms. However, these problem instances introduce biases in the comparison outcomes, which is often not taken into account. The confidence of the comparison can be strengthened by using statistical… Read more: Multi-Objective Statistically Robust Algorithm Ranking
Jeroen G. Rook – University of Twente PhD candidate Comparing algorithms is a non-trivial task. Often, a set of representative problem instances are used to compare algorithms. However, these problem instances introduce biases in the comparison outcomes, which is often not taken into account. The confidence of the comparison can be strengthened by using statistical… Read more: Multi-Objective Statistically Robust Algorithm Ranking - Deep fake videos detection through Explainable AI
 Aiming towards combating the challenges faced by fake video detection, the prime objective of this research is to develop a proactive, advanced explainable, human collaborated AI-based online disinformation detecting tool for securing a trustworthy social media environment.
Aiming towards combating the challenges faced by fake video detection, the prime objective of this research is to develop a proactive, advanced explainable, human collaborated AI-based online disinformation detecting tool for securing a trustworthy social media environment. - Modeling others for cooperation under imperfect information
 Nieves Montes PhD Student at Artificial Intelligence Research Institute (IIIA-CSIC) This research visit will focus on models for empathetic software agents. This means embedding autonomous agents with the ability to model their peers and understand the reasons behind their behaviour. This work is to enhance the performace of agents in cooperative tasks, where they need… Read more: Modeling others for cooperation under imperfect information
Nieves Montes PhD Student at Artificial Intelligence Research Institute (IIIA-CSIC) This research visit will focus on models for empathetic software agents. This means embedding autonomous agents with the ability to model their peers and understand the reasons behind their behaviour. This work is to enhance the performace of agents in cooperative tasks, where they need… Read more: Modeling others for cooperation under imperfect information - Logic-based multi-agent reinforcement learning
 Brian Logan Associate Professor at Utrecht University Many activities that are easy for humans, such as walking together with other humans, are hard to program as a set of rules for Artificial Intelligence (AI) robots. This is why machine learning is so popular in AI: correct behaviour can be learned by trial and error. However,… Read more: Logic-based multi-agent reinforcement learning
Brian Logan Associate Professor at Utrecht University Many activities that are easy for humans, such as walking together with other humans, are hard to program as a set of rules for Artificial Intelligence (AI) robots. This is why machine learning is so popular in AI: correct behaviour can be learned by trial and error. However,… Read more: Logic-based multi-agent reinforcement learning - Conformal Inference for multivariate, complex, and heterogeneous data
 Marcos Matabuena University of Santiago de Compostela In this project, in collaboration with Gábor Lugosi (UPF), we propose new uncertainty quantification methods based on the design of new Conformal Inference strategies for complex data that arise in modern personalized medicine applications. The new uncertainty methods can examine the reliability and safety of results obtained with… Read more: Conformal Inference for multivariate, complex, and heterogeneous data
Marcos Matabuena University of Santiago de Compostela In this project, in collaboration with Gábor Lugosi (UPF), we propose new uncertainty quantification methods based on the design of new Conformal Inference strategies for complex data that arise in modern personalized medicine applications. The new uncertainty methods can examine the reliability and safety of results obtained with… Read more: Conformal Inference for multivariate, complex, and heterogeneous data - Neuro-symbolic integration for graph data
 Manfred Jaeger Associated Professor at Aalborg University From Social networks to bibliographic databases: many important real-world phenomena consist of networks of connected entities. The mathematical model of such networks is that of a graph, which in its basic form just consists of a collection of nodes that are connected by edges. To model the rich… Read more: Neuro-symbolic integration for graph data
Manfred Jaeger Associated Professor at Aalborg University From Social networks to bibliographic databases: many important real-world phenomena consist of networks of connected entities. The mathematical model of such networks is that of a graph, which in its basic form just consists of a collection of nodes that are connected by edges. To model the rich… Read more: Neuro-symbolic integration for graph data - Private Continual Learning from a Stream of Pretrained Models
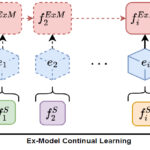 Antonio Carta Post-doc at Pisa University Learning continually from non-stationary data streams is a challenging research topic of growing popularity in the last few years. Being able to learn, adapt and generalize continually, in an efficient, effective and scalable way appears to be fundamental for a more sustainable development of Artificial Intelligent systems. However, access… Read more: Private Continual Learning from a Stream of Pretrained Models
Antonio Carta Post-doc at Pisa University Learning continually from non-stationary data streams is a challenging research topic of growing popularity in the last few years. Being able to learn, adapt and generalize continually, in an efficient, effective and scalable way appears to be fundamental for a more sustainable development of Artificial Intelligent systems. However, access… Read more: Private Continual Learning from a Stream of Pretrained Models - Matheuristic Techniques for Timetabling Problems
 Roberto Maria Rosati PhD Student in Information Engineering at University of Udine Recently, matheuristics have emerged as a promising research branch in combinatorial optimization. Thanks to this collaboration supported by TAILOR connectivity fund, we will design and apply novel matheuristic techniques to a variety of timetabling problems that are under investigation at University of Udine.… Read more: Matheuristic Techniques for Timetabling Problems
Roberto Maria Rosati PhD Student in Information Engineering at University of Udine Recently, matheuristics have emerged as a promising research branch in combinatorial optimization. Thanks to this collaboration supported by TAILOR connectivity fund, we will design and apply novel matheuristic techniques to a variety of timetabling problems that are under investigation at University of Udine.… Read more: Matheuristic Techniques for Timetabling Problems - 1st International Joint Conference on Learning & Reasoning
 Nikos Katzouris National Center for Scientific Research “Demokritos” The rapid progress in machine learning has been the primary reason for a fresh look in the transformative potential of AI as a whole during the past decade. A crucial milestone for taking full advantage of this potential is the endowment of algorithms that learn from experience… Read more: 1st International Joint Conference on Learning & Reasoning
Nikos Katzouris National Center for Scientific Research “Demokritos” The rapid progress in machine learning has been the primary reason for a fresh look in the transformative potential of AI as a whole during the past decade. A crucial milestone for taking full advantage of this potential is the endowment of algorithms that learn from experience… Read more: 1st International Joint Conference on Learning & Reasoning - Trustworthy and sample efficient computer vision
 Mohammadreza Amirian Research assistant, Zurich University of Applied Sciences (ZHAW) After the breakthrough of transformers in the context of natural language processing, these models are now being adapted for computer vision and image classification tasks. Transformer-based models showed at least equal descriptive properties compared with convolutional models, however, initial specimen required a larger amount of… Read more: Trustworthy and sample efficient computer vision
Mohammadreza Amirian Research assistant, Zurich University of Applied Sciences (ZHAW) After the breakthrough of transformers in the context of natural language processing, these models are now being adapted for computer vision and image classification tasks. Transformer-based models showed at least equal descriptive properties compared with convolutional models, however, initial specimen required a larger amount of… Read more: Trustworthy and sample efficient computer vision - Conflict Resolution Algorithm for the Ethics of AI
 Réka Markovich Post-doctoral Researcher at Luxemburg University The ethical rules for the so-called moral behavior of AI tools are a major concern, and each AI tool has multiple stakeholders with possibly different moral backgrounds and expectations. How should we decide whose moral expectations these tools should meet? Réka Markovich’s research stay, financed by the TAILOR… Read more: Conflict Resolution Algorithm for the Ethics of AI
Réka Markovich Post-doctoral Researcher at Luxemburg University The ethical rules for the so-called moral behavior of AI tools are a major concern, and each AI tool has multiple stakeholders with possibly different moral backgrounds and expectations. How should we decide whose moral expectations these tools should meet? Réka Markovich’s research stay, financed by the TAILOR… Read more: Conflict Resolution Algorithm for the Ethics of AI